I/O 多路复用可以复用线程的处理能力,让单个线程也可以处理大量并发请求。目前 Linux 提供了三种 I/O 多路复用方式,分别为 SELECT,POLL,EPOLL。
1. Select
Select 是最常用的一种 IO 多路复用机制,可以一次检查多个文件描述符的状态。
1.1 示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/select.h>
int
main(void)
{
int retval;
fd_set rfds;
struct timeval tv;
/* Watch stdin (fd 0) to see when it has input. */
FD_ZERO(&rfds);
FD_SET(0, &rfds);
/* Wait up to five seconds. */
tv.tv_sec = 5;
tv.tv_usec = 0;
retval = select(1, &rfds, NULL, NULL, &tv);
/* Don't rely on the value of tv now! */
if (retval == -1)
perror("select()");
else if (retval)
printf("Data is available now.\n");
/* FD_ISSET(0, &rfds) will be true. */
else
printf("No data within five seconds.\n");
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
1.2 NFDS 数据结构
Select 用 fd_set 来标记文件描述符的状态,fd_set 是一个结构体里面 __fds_bits 用于保存 File Descriptor 的状态。__fds_bits 是一个数组,所占空间为 128 个字节,也就是 1024 bit。
/* fd_set for select and pselect. */
typedef struct
{
/* XPG4.2 requires this member name. Otherwise avoid the name
from the global namespace. */
#ifdef __USE_XOPEN
__fd_mask fds_bits[__FD_SETSIZE / __NFDBITS];
# define __FDS_BITS(set) ((set)->fds_bits)
#else
__fd_mask __fds_bits[__FD_SETSIZE / __NFDBITS];
# define __FDS_BITS(set) ((set)->__fds_bits)
#endif
} fd_set;
其中一个 bit 用来表示一个 File Descriptor 的状态,所以说在 Socket 网络编程中 Select 实际上最多也只能处理 1023 个链路。Select 中采用的几个宏都是用于操作这个 fd_set 的。
/* Access macros for `fd_set'. */
#define FD_SET(fd, fdsetp) __FD_SET (fd, fdsetp)
#define FD_CLR(fd, fdsetp) __FD_CLR (fd, fdsetp)
#define FD_ISSET(fd, fdsetp) __FD_ISSET (fd, fdsetp)
#define FD_ZERO(fdsetp) __FD_ZERO (fdsetp)
其具体的实现如下
/* We don't use `memset' because this would require a prototype and
the array isn't too big. */
#define __FD_ZERO(s) \
do { \
unsigned int __i; \
fd_set *__arr = (s); \
for (__i = 0; __i < sizeof (fd_set) / sizeof (__fd_mask); ++__i) \
__FDS_BITS (__arr)[__i] = 0; \
} while (0)
#define __FD_SET(d, s) \
((void) (__FDS_BITS (s)[__FD_ELT(d)] |= __FD_MASK(d)))
#define __FD_CLR(d, s) \
((void) (__FDS_BITS (s)[__FD_ELT(d)] &= ~__FD_MASK(d)))
#define __FD_ISSET(d, s) \
((__FDS_BITS (s)[__FD_ELT (d)] & __FD_MASK (d)) != 0)
可以看到 FD_ZERO 就是循环将 __fds_bits全部置零,FD_SET 与 FD_CLR 就是通过 File Descriptor 的值计算的数组的下标,以及通过掩码操作对应的位。从这里也可以看出,如果 File Descriptor 的值大于 1024,__FDS_BITS (s)[__FD_ELT(d)] 就可能会计算出重复的值,导致程序运行出现异常。所以需要处理大量 Socket File descriptor 的场景最好不要使用 Select。
在使用 select 的时候还有一点需要注意的是,select 会在原地修改 rfds,所以在每次调用 select 之前都需要将需要监听的 File Descriptor 重新 FD_SET。
2. POLL
POLL 与 Select 的功能相似,都是一次可以检查多个文件描述符的状态。但是与 SELECT 的固定大小的 NFDS 不同,POLL 的 NFDS 是由用户自行分配的,所以 POLL 没有最大文件描述符的限制。
2.1 示例
/* poll_input.c
Licensed under GNU General Public License v2 or later.
*/
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <poll.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define errExit(msg) do { perror(msg); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \
} while (0)
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int ready;
char buf[10];
nfds_t num_open_fds, nfds;
ssize_t s;
struct pollfd *pfds;
if (argc < 2) {
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s file...\n", argv[0]);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
num_open_fds = nfds = argc - 1;
pfds = calloc(nfds, sizeof(struct pollfd));
if (pfds == NULL)
errExit("malloc");
/* Open each file on command line, and add it to 'pfds' array. */
for (nfds_t j = 0; j < nfds; j++) {
pfds[j].fd = open(argv[j + 1], O_RDONLY);
if (pfds[j].fd == -1)
errExit("open");
printf("Opened \"%s\" on fd %d\n", argv[j + 1], pfds[j].fd);
pfds[j].events = POLLIN;
}
/* Keep calling poll() as long as at least one file descriptor is
open. */
while (num_open_fds > 0) {
printf("About to poll()\n");
ready = poll(pfds, nfds, -1);
if (ready == -1)
errExit("poll");
printf("Ready: %d\n", ready);
/* Deal with array returned by poll(). */
for (nfds_t j = 0; j < nfds; j++) {
if (pfds[j].revents != 0) {
printf(" fd=%d; events: %s%s%s\n", pfds[j].fd,
(pfds[j].revents & POLLIN) ? "POLLIN " : "",
(pfds[j].revents & POLLHUP) ? "POLLHUP " : "",
(pfds[j].revents & POLLERR) ? "POLLERR " : "");
if (pfds[j].revents & POLLIN) {
s = read(pfds[j].fd, buf, sizeof(buf));
if (s == -1)
errExit("read");
printf(" read %zd bytes: %.*s\n",
s, (int) s, buf);
} else { /* POLLERR | POLLHUP */
printf(" closing fd %d\n", pfds[j].fd);
if (close(pfds[j].fd) == -1)
errExit("close");
num_open_fds--;
}
}
}
}
printf("All file descriptors closed; bye\n");
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
2.1 POLL Event
POLL 由很多事件,但是在实际的编程中最常用的还是 POLLIN 与 POLLOUT,其他的基本上没有用过。
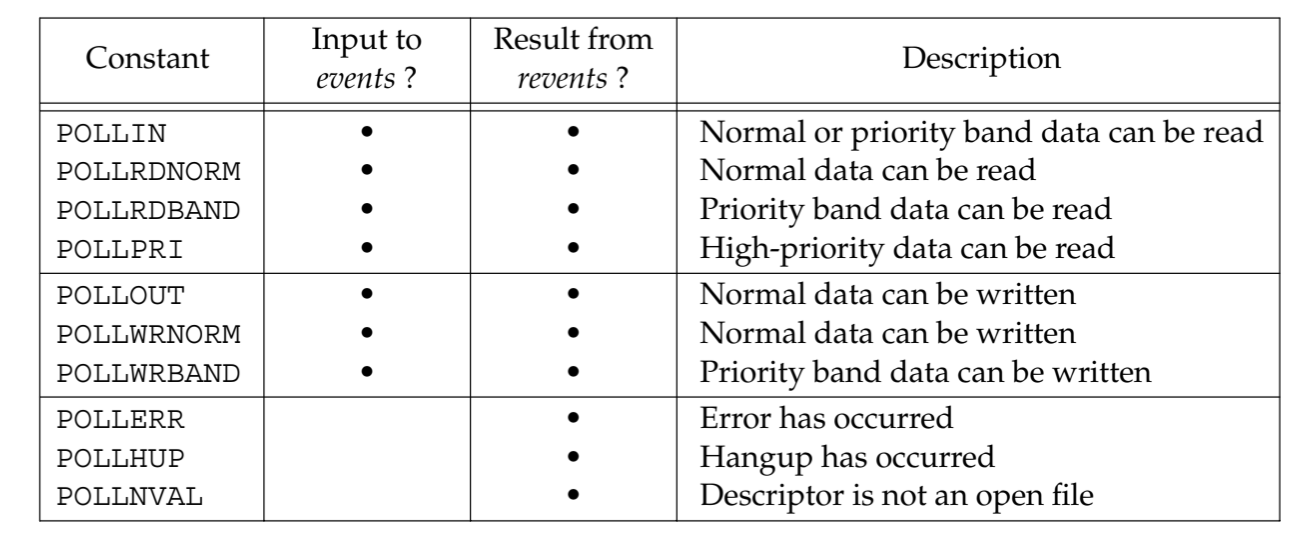
2.2 POLL Vs SELECT
- Select 的 NFDS 采用的是 bit mast 有最大的文件描述符限制,而 POLL 是由用户来分配的数组,理论上是没有限制的
- Select 的 NFDS 在调用
select函数之后会被原地修改,之后得重新调用FD_SET。POLL 的返回事件则在revents中,不会影响其他字段。
3. EPOLL
EPOLL 的功能功能与上面的 SELECT 和 POLL 都是一样的,但是在原来 POLL 的基础上优化了不少地方。
3.1 示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#define PORT 8888
#define MAX_EVENTS 10
#define BUFFER_SIZE 1024
int handleConn(int client_fd)
{
char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE];
struct sockaddr_in address;
socklen_t addrlen = sizeof(address);
int valread = read(client_fd, buffer, BUFFER_SIZE);
if (valread == 0)
{
getpeername(client_fd, (struct sockaddr *)&address, &addrlen);
printf("Client disconnected: IP %s, PORT %d\n",
inet_ntoa(address.sin_addr), ntohs(address.sin_port));
close(client_fd);
return -1;
}
else
{
buffer[valread] = '\0';
printf("Received from client: %s\n", buffer);
send(client_fd, buffer, valread, 0);
}
return 1;
}
int main()
{
int server_fd, client_fd, epoll_fd;
struct sockaddr_in address;
struct epoll_event ev, events[MAX_EVENTS];
int addrlen = sizeof(address);
// 创建服务器套接字
if ((server_fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0)) == 0)
{
perror("Socket creation failed");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
address.sin_family = AF_INET;
address.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY;
address.sin_port = htons(PORT);
// 绑定地址到服务器套接字
if (bind(server_fd, (struct sockaddr *)&address, sizeof(address)) < 0)
{
perror("Bind failed");
close(server_fd);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// 开始监听
if (listen(server_fd, 3) < 0)
{
perror("Listen failed");
close(server_fd);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("Listening on port %d...\n", PORT);
// 创建 epoll 实例
if ((epoll_fd = epoll_create1(0)) < 0)
{
perror("Epoll creation failed");
close(server_fd);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// 添加服务器套接字到 epoll
ev.events = EPOLLIN;
ev.data.fd = server_fd;
if (epoll_ctl(epoll_fd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, server_fd, &ev) < 0)
{
perror("Epoll add server socket failed");
close(server_fd);
close(epoll_fd);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
while (1)
{
int event_count = epoll_wait(epoll_fd, events, MAX_EVENTS, -1);
if (event_count < 0)
{
perror("Epoll wait error");
break;
}
for (int i = 0; i < event_count; i++)
{
if (events[i].data.fd == server_fd)
{
// 处理新连接
client_fd = accept(server_fd, (struct sockaddr *)&address, (socklen_t *)&addrlen);
if (client_fd < 0)
{
perror("Accept failed");
continue;
}
printf("New connection: socket fd %d, IP %s, PORT %d\n",
client_fd, inet_ntoa(address.sin_addr), ntohs(address.sin_port));
// 添加新客户端套接字到 epoll
ev.events = EPOLLIN;
ev.data.fd = client_fd;
if (epoll_ctl(epoll_fd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, client_fd, &ev) < 0)
{
perror("Epoll add client socket failed");
close(client_fd);
}
}
else
{
// 处理客户端数据
client_fd = events[i].data.fd;
int rt = handleConn(client_fd);
if (rt < 0)
{
// 客户端断开连接,从 epoll 移除套接字
epoll_ctl(epoll_fd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, client_fd, NULL);
}
}
}
}
close(server_fd);
close(epoll_fd);
return 0;
}
3.1 EPOLL 原理
-
epoll_create在文件系统中创建一个 epoll 的文件描述符,并创建一个红黑树用于存储以后
epoll_ctl传来的文件描述符,以及一个 list 用于存储准备就绪的事件 -
epoll_ctl将文件描述符添加到对应的红黑树上面,给内核的终端处理函数注册一个回调函数,如果该文件描述符的中断到了,就把他放到就绪的 list 中
-
epoll_wait观察就绪列表中是否有数据,有数据就返回没有就sleep。
3.1 EPOLL Vs POLL
-
SELECT 与 POLL,在收到事件通知之后都需要将等待列表遍历一遍,才能找出真正产生事件的文件描述符,如果存在大量非活跃的链路这样是非常耗时间的。EPOLL 采用的方式为内核来维护这个等待列表,用户只需要通过
epoll_ctl来添加感兴趣的文件标识符即可,在收到事件之后用户也只需要遍历实际产生事件的列表。所以在处理大量非活跃链路的时候 EPOLL 的性能会远高于 POLL 和 SELECT。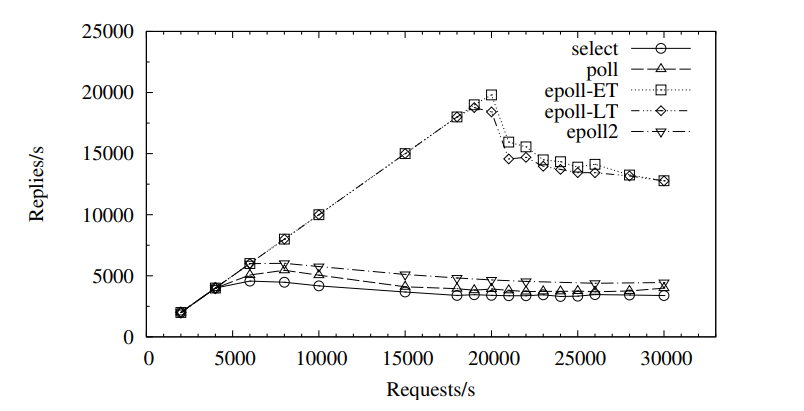
-
在没有空闲连接的场景下,EPOLL 的回调机制性能可能还要比 POLL 和 SELECT 差一些。
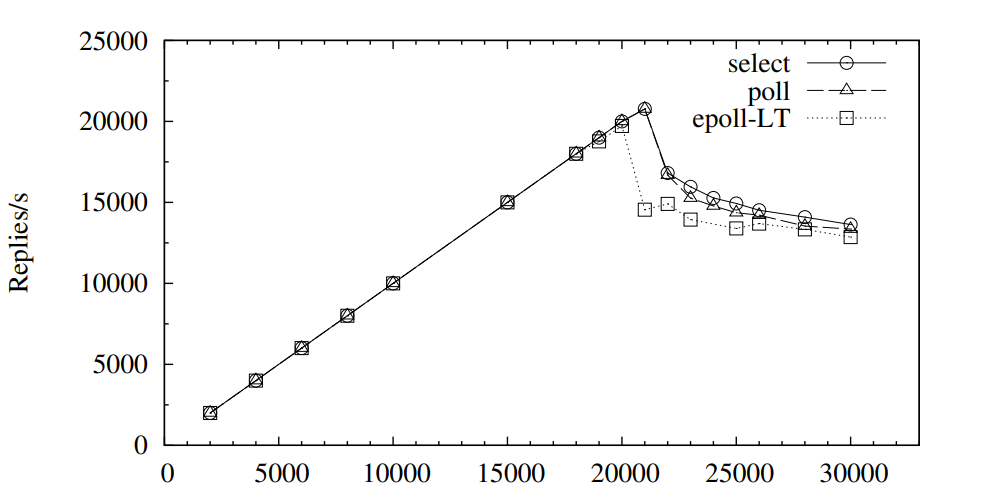
3.4 边缘触发与水平触发
SELECT 与 POLL 都只有水平触发模式,EPOLL 同时支持水平触发与边缘触发,默认是使用水平触发。水平触发是指,只要满足信号触发条件就一直会有信号返回。边缘触发是指只有状态发生变化的时候才会有事件返回,比如从不可读切换到可读就会有事件返回,但是从可读到可读不会有事件返回。
所以在使用边缘触发的时候必须要使用非堵塞 IO,收到可读信号的时候就得将数据全部读完,否则后面可能会收不到可读信号了,导致丢包。还有一点需要注意的是,当使用了非杜塞 IO 之后,必须要使用应用层的 Write Buffer,因为在非堵塞 IO 的情况下,用 write 函数并不一定可以发送完成,此时就需要将数据存储在应用层 Buffer 中等待,可写信号过来将所有应用层数据全部写入。
综上所述在使用边缘触发虽然说可能会提升一些性能,但是会大大的增加复杂度,使用的时候得小心些。
